Accessibility
Designing with Accessibility in Mind
Universal Design for Learning (UDL) encourages instructors to design courses that are usable by everyone regardless of learning style of preference. It asks us to consider factors like age, ability, and diverse needs, and to curate learning environments that are adaptable and intuitive. You can also read through this quick Universal Design Cheat Sheet.
Accessibility requires instructors to create learning environments that are usable by people with disabilities who often require specific adaptations or accommodations to meet individual needs. This might involve providing assistive technologies or making adjustments to existing designs.
The Key Differences between UDL and Accessibility is that while both aim for inclusivity, UDL designs for a wide range of users while accessibility addresses the specific needs of people with disabilities through accommodations.
Why accessibility is vital: As instructors, it is our job to ensure that our students' learning needs are being met. By including accessibility tools and practices in our classrooms, we're working towards equality and a more supportive campus.
Learn what to do
Electronic Accessibility Rubric
Here you can review varying levels of accessibility related to different learner needs.
Best Practices
Here you'll find an overview of which accessibilty tools you might incorporate for various learning needs.
Core Concepts
Here you'll find an overview of the "what," the "why," and the "how" of different accessibility tools.
MSU Campus Standards
Here you can find MSU's campus standards in relation to accessibility.
Why Accessibility Matters
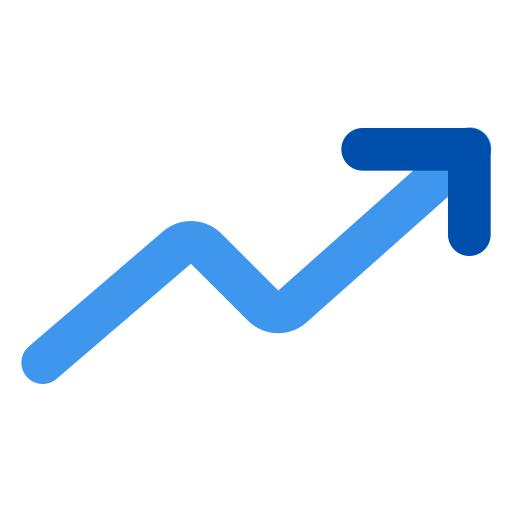


1 in 5 college students
has a disability
Reported disabilities increased
from 11% to 21%
3.5 million college students
have a disability
Accessibility News

Creating a Culture of Inclusion
When developing a culture of inclusion, colleges and universities have specific responsibilities to students with disabilities to ensure they can learn and achieve their goals.

Rise in College Students with Disabilities
Primarily due to mental health issues or attention deficit disorders, the percentage of college students with disabilities increased from 11% to 21% between 2004 and 2020.

Disability and Higher Education
Students with disabilities face extra steps in higher education, carrying the responsibility of navigating what they need both inside and outside the classroom...[this article] will explore these complexities and offer recommendations for creating a more inclusive campus environment.
